Robust Preclinical Data Support Advancement of our Duchenne Programs
In preclinical studies, our EEV-Oligonucleotide approach has led to:
~41,000 people in the U.S. and Europe have Duchenne.1-2
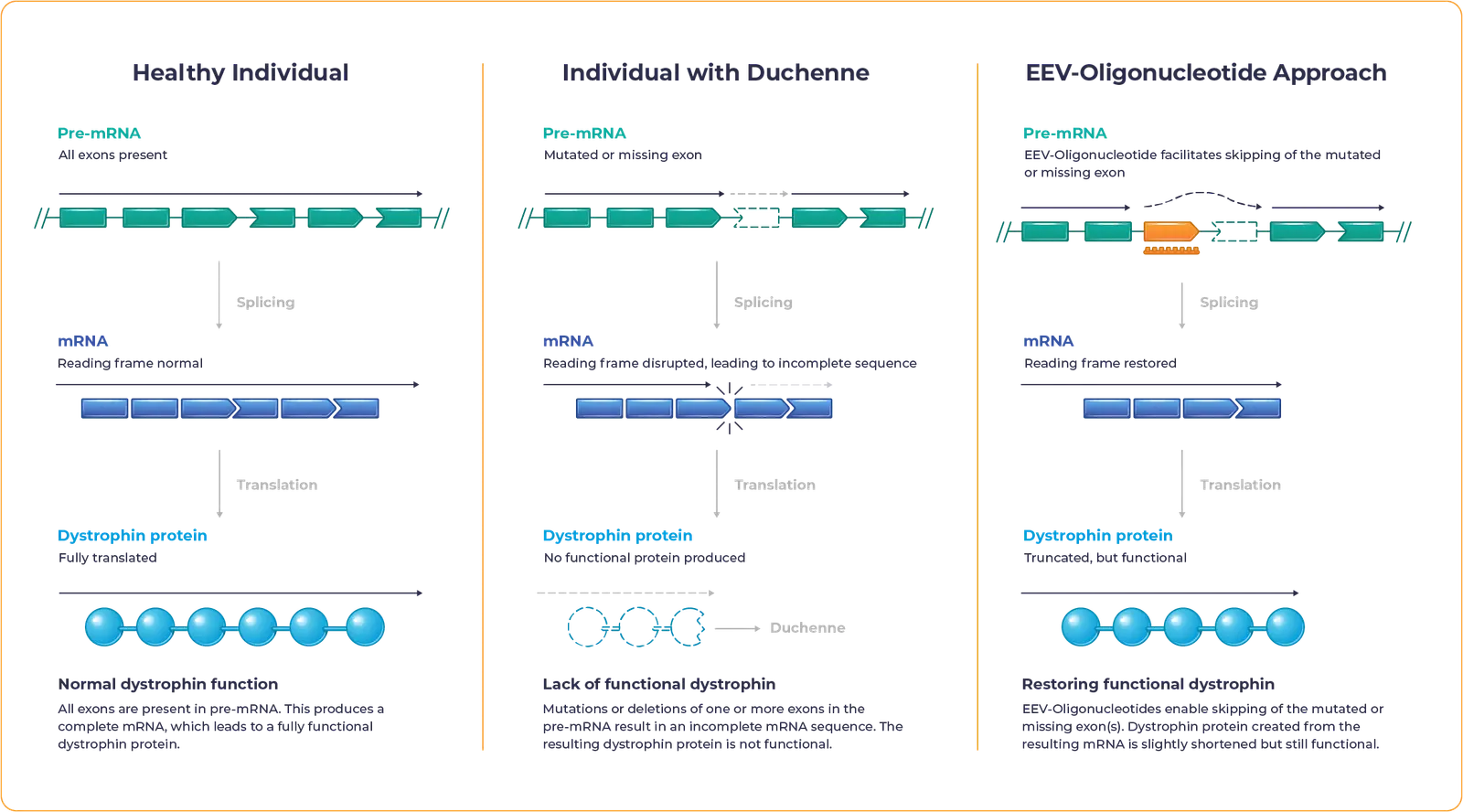
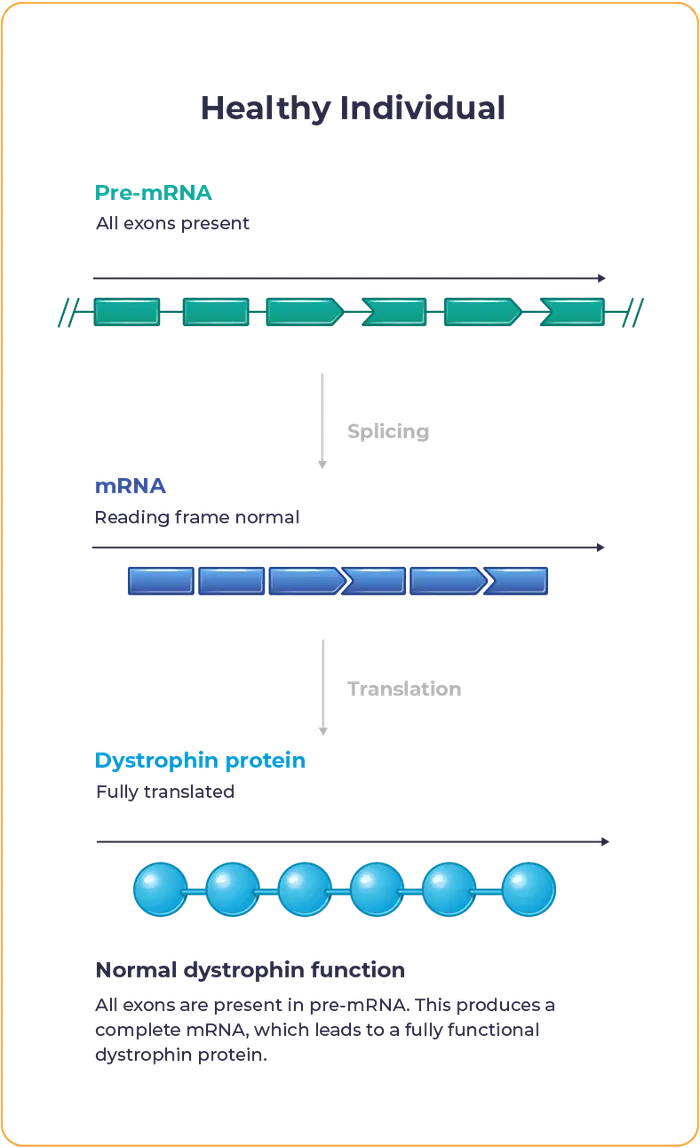
Duchenne muscular dystrophy – often referred to as Duchenne or DMD – is a rare disease caused by mutations in the DMD gene, which encodes for the dystrophin protein. These mutations lead to inadequate dystrophin production.
Dystrophin is essential to maintaining the structural integrity and function of muscle cells.
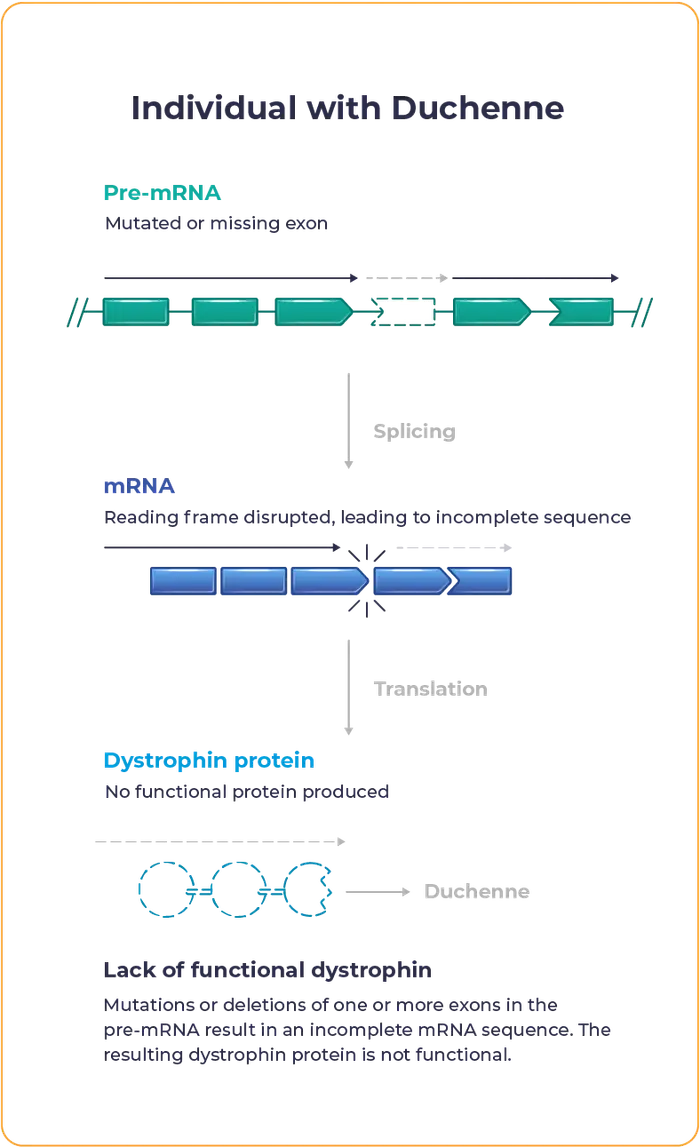
Lack of functional dystrophin leads to progressive loss of muscle strength, impacting mobility and causing heart or respiratory complications that contribute to high mortality rates.
Currently approved exon skipping therapies for Duchenne have not shown considerable increases in dystrophin production and often fail to widely distribute across muscle tissue.3-6
Our proprietary EEV-Oligonucleotide is designed to address the underlying genetic cause of Duchenne to allow muscle cells to produce functional dystrophin.
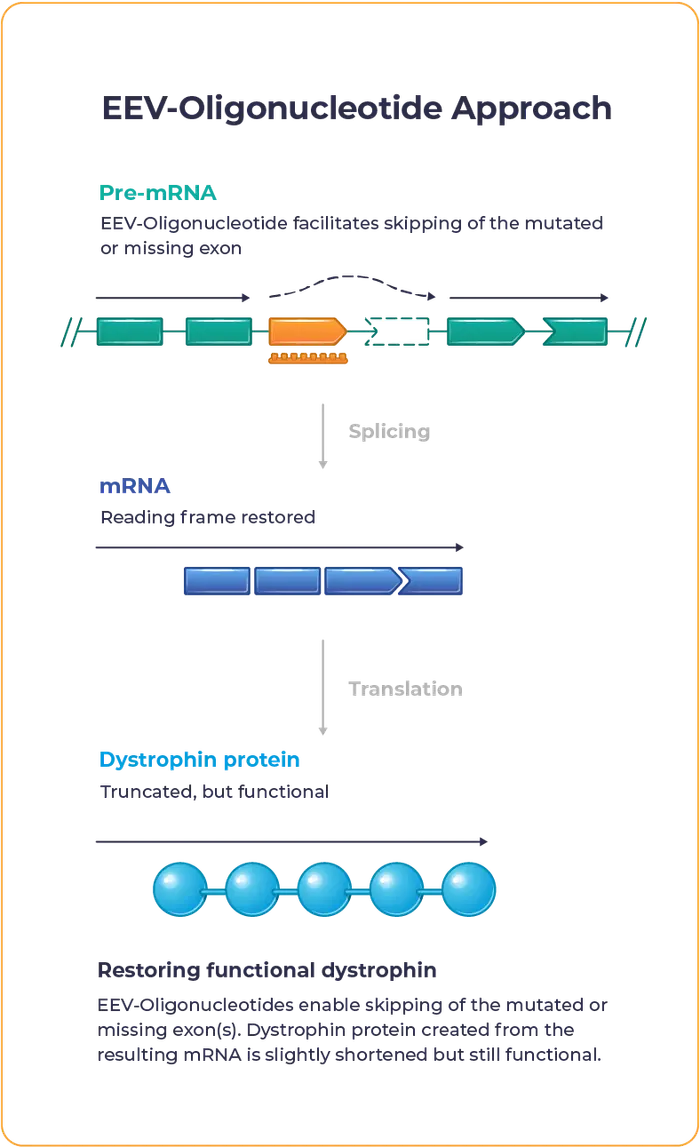
Entrada’s lead oligonucleotide programs include ENTR-601-44, ENTR-601-45 and ENTR-601-50 for the potential treatment of people living with Duchenne muscular dystrophy who are exon 44, 45 and 50 skipping amenable, respectively.
In preclinical studies, our EEV-Oligonucleotide approach has led to:
Visit our Manuscripts and Presentations pages to learn more
Parent Project Muscular Dystrophy. About Duchenne. Accessed November 2024.
European Medicines Agency. EU3202375 Orphan Designation. Accessed November 2024.
AMONDYS 45 [package insert]. Cambridge, MA: Sarepta Therapeutics, Inc.; 2021.
VILTEPSO [package insert]. Paramus, NJ: NS Pharma, Inc.; 2020.
VYONDYS 53 [package insert]. Cambridge, MA: Sarepta Therapeutics, Inc.; 2019.
EXONDYS 51 [package insert]. Cambridge, MA: Sarepta Therapeutics, Inc.; 2016.